Solar panels harness the sun's energy and convert it into electrical energy that can then be utilized to power different purposes within a home. Solar panel systems are a viable option to generate electricity, especially in off-grid areas where electricity grids aren't being serviced.
If properly maintained, solar panel systems are considerably less expensive and will generate energy for three decades. With the changing climate globally, it is becoming more essential to make the most effective move to reduce the pressure on our environment to reduce the release of greenhouse gases.
You may know that solar photovoltaic (PV) panels convert the sun's energy into electricity, but do you know the technology behind it. In this article's final paragraph, you'll clearly understand how do solar panel works. Let's begin!
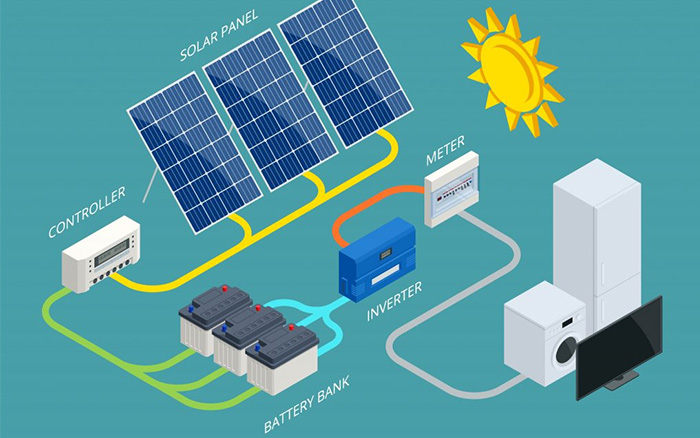
The Basics of Solar Energy Generation and Transmission

- The direct sunlight strikes the solar panels and creates an electric field.
- The flow of electricity is controlled by the electricity. It flows through the panel and then into the wiring.
- The wire delivers the power to the inverter, which is transformed into DC into AC electricity, which is then used to power the properties.
- When energy flows through the meter, it causes it to run backwards, crediting the excess power generation to a building.
What exactly are Solar Panels?

Solar panels, sometimes called Solar PV panels, convert sunlight directly and capture particles of energy called photons, which power electrical devices. They can power various applications like remote power systems cabins, remote sensing, telecommunication equipment and electricity production through commercial and residential solar electrical systems. There are may advantages of solar energy. It is clean and nature friendly.
What are some benefits of solar energy?

- There's 14.6GW of solar power installed in the USA, four times more capacity than Britain's biggest power station powered by fossil fuels.
- The panels can be placed in a variety of locations. From larger, rural solar farms that help to help the local ecosystem by providing a natural habitat for butterflies, bees and nesting birds to rooftop solar panels in urban centres that help fight the problem of fuel poverty.
- They don't create any sound pollution when they generate electricity. This means installations will be smooth in busy urban areas or quiet rural locations.
- Solar panels are incredibly secure. They're made mostly of silicon sheets, and photovoltaic radiation is not dangerous.
- +aic cells leak or emit any fumes or toxins.
Do solar panels work on cloudy days?

Solar panels respond to the visible spectrum of light. This means that if it's visible enough, there's enough light for them to begin producing electricity. However, the more intense the sunlight is, the greater the power solar panels generate.
Does it have to be warm for solar panels to function?

Solar panels generate more electricity during the summer months, and this can make it appear as if they require warmer temperatures to function. But this isn't true. It's more that the stronger sun and warmer temperatures typically coincide. In fact, when the temperature becomes excessively high (or too cold), they will be less effective.
We get more than 8 hours of sun each day throughout the year and don't have to worry about extreme temperatures. The USA is ideally suited for solar power.
The science behind how solar panels and solar energy work: solar cells and the photovoltaic effect
In simple terms, solar panels generate electricity when the particles of sunlight, also known as photons, knock electrons out from atoms and set them into motion. The electrons' movement creates electricity. Solar panels are designed to capture and transform this flow into usable electric current. It is the primary physical and chemical process that underlies most solar technology.
The photovoltaic effect: how does it work
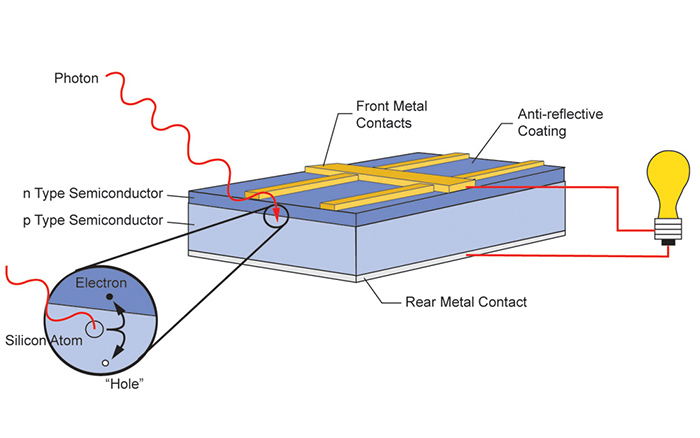
The science behind generating electricity using solar panels comes from the photovoltaic effect. The first discovery of it was made by Edmond Becquerel in 1839. The photovoltaic effect is generally seen as one of the characteristics of certain types of materials (known as semiconductors), allowing them to create an electric current when exposed to sunlight.
The photovoltaic effect operates through the following steps:
- The sun's rays hit the solar cells, activating electrons within the cells and putting them into motion.
- The electrons escape from the cell layer junction, creating an electrical current.
- Wires and metal plates can capture electrons and produce electricity.
The process of creating solar energy begins by using solar cells. These are the tiny pieces that form a larger solar panel. Solar cells typically comprise silicon (atomic #14 on the periodic table). Silicon is a non-metal semiconductor that can absorb sunlight and convert it into electricity. We also utilize silicon in nearly every computer in the world. Many kinds of semiconductors are commonly employed in solar cells, and silicon is the most widely used in almost all solar cells produced today.
Cadmium-telluride, as well as copper indium gallium diselenide, are two of the most common semiconductors that are used in the production of thin-film solar panels.
Two layers of silicon are utilized in photovoltaic cells. Each one is specialized or "doped" to create an electric field at the junction of the layers. The electric field causes loose electrons to move throughout the solar cell before exiting the silicon junction, completing the electrical current. The two elements, boron and phosphorus, are frequently utilized as negative and positive doping agents, respectively, to form a photovoltaic's negative and positive side.
Alternatives to solar panels made of silicon
Though silicon is the most commonly used semiconductor in solar panels, other options are utilized in some of the new and upcoming solar-powered products used in the solar sector.
The thin-film solar cells are a broad class of solar cells made from flexible and light materials. There are four major chemical types of solar cells with thin film, including cadmium Telluride (CdTe), Amorphous silicon (a-Si) copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) and gallium arsenide (GaAs). The light-absorbing layers of these kinds of cells are about 350 times smaller than silicon ones, which is why they are given the term "thin film."
Organic solar cells are a distinct thin-film solar cell that uses carbon-based substances as semiconductors. Organic photovoltaics (OPV) are sometimes called "plastic solar cells" or "polymer solar cells" and are created by dissolving organic compounds into ink and printing them on thin plastics.
Perovskite solar cells are a third type of solar cells made using perovskites. They are a type of manufactured material with a unique crystallographic pattern that makes them highly efficient in converting photons of sunlight into electricity usable. Perovskite cells are constructed by "solution processing", a similar process used to print newspapers.
You can go solar with confidence, thanks to Arise Solar.
Suppose you want to lower your carbon footprint and start saving money on electricity. In that case, you'll need to look at solar panel estimates. This is where Arise Solar can help: go to our website and filled out the form for an easy quote. At Arise Solar, we provide you with a customized quote from the installers in your area. What are you waiting for? Start your renewable energy journey with Arise Solar llc today!
